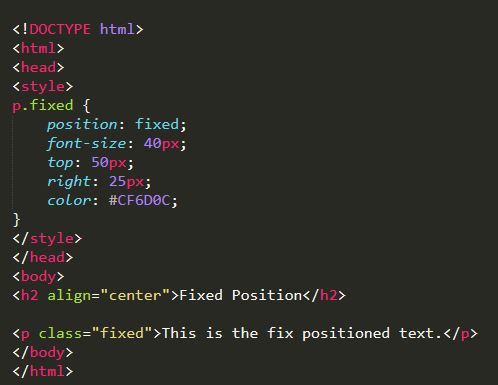
Relative, absolute and fixed are three types of position properties used in CSS. Position properties define how elements are positioned on a webpage. Positioning allows the web developer to take elements out of their normal flow on a web page and change their behaviour e.g. elements displaying side by side, remaining in a fixed position when scrolling. The positioning attributes top, bottom, left and right are used to specify exacty where to move the positioned element. Static is the default positioning for elements on a webpage.
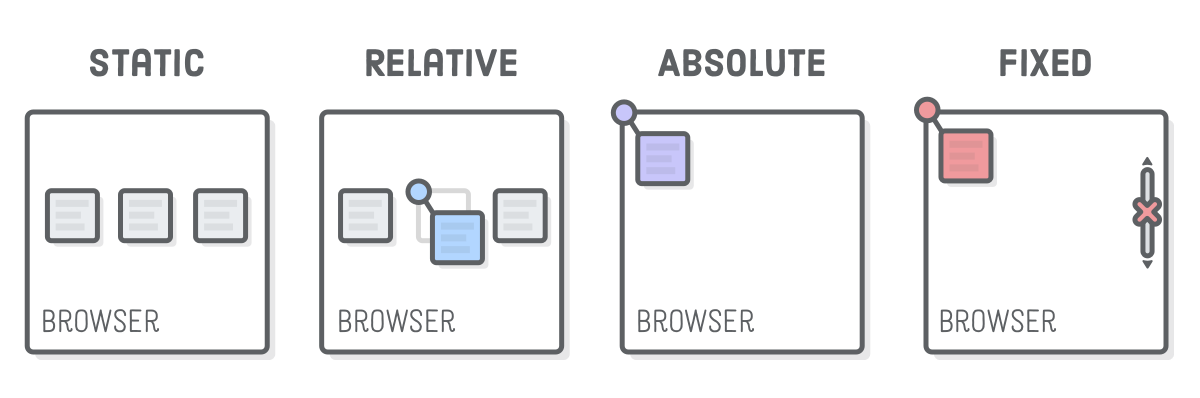
Relative:
An element is positioned relative to its normal (static) position, or in other words, relative to itself. If you set position relative without changing positioning attributes (top, bottom, left, right) it will remain in the same position as if it were static. However, if you add positioning attributes e.g. top: 20px; left 20px, an element will move down from the top 20px and away from the left 20px relative to its normal position on the webpage.
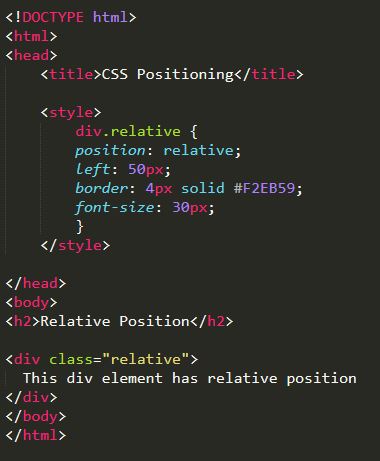
Absolute:
Allows an element to be placed in an exact position on a webpage using the aformentioned positioning attributes to set the location. However, the element will display relative to the next parent element with relative or absolute positioning. If there is no such parent it will be placed relative to the page itself
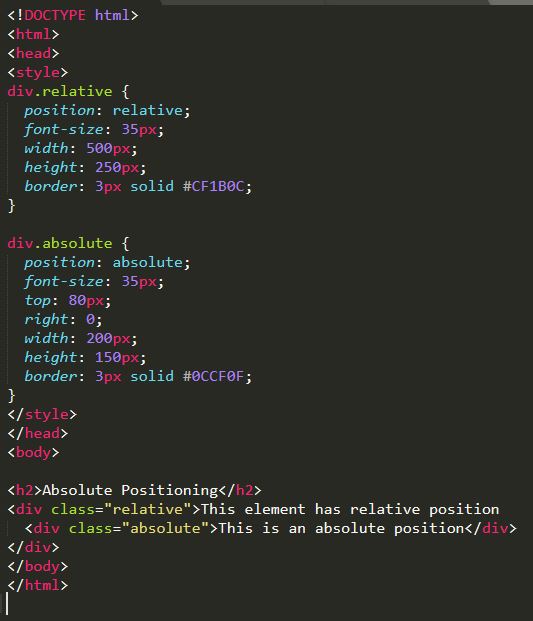
Fixed:
An element is positioned relative to the viewport or the browser window itself. When scrolling through a webpage the element position stays the same in the viewport. This can be incredibly useful for positioning a menu that you want the user to always have access to. However, one must be careful to crate enough space between elements as fixed elements can overlap and make make other elements inaccessable